Understanding the differences between Optical Access and traditional fiber technology can be crucial for deploying modern networks. These two types of technologies are foundational in contemporary data transmission systems. They play significant roles in enterprises, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and Multiple System Operators (MSOs). This blog delves into both technologies to help you identify which one is better suited for your network needs.

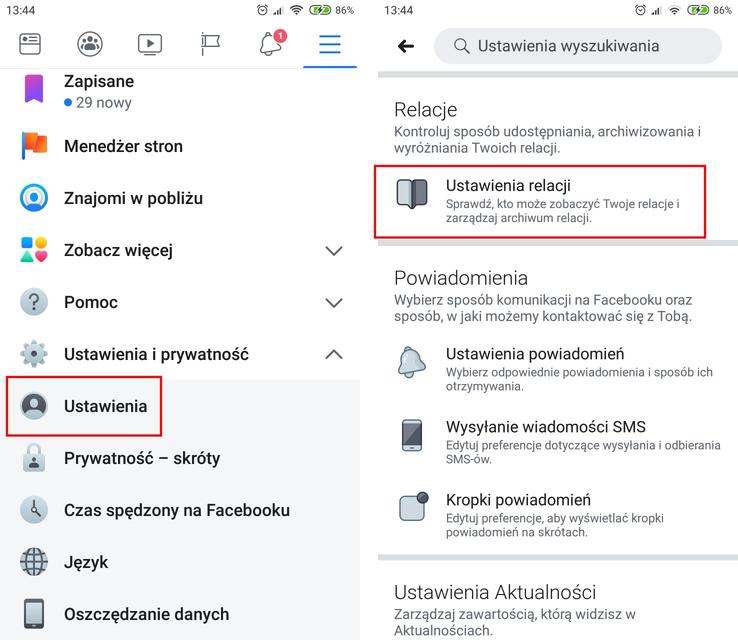
What is Optical Access and How Does It Work?
Core Components of Optical Access
Optical access, often referred to as optical fiber access, uses Passive Optical Network (PON) technology. This technology provides high-speed data transmission and higher bandwidth capabilities. Huawei’s OptiXaccess solutions exemplify this technology, employing components like Optical Line Terminals (OLTs) and Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) to create efficient data pathways. For instance, the Huawei SmartAX MA5800 series supports services like 4K/8K/VR, ensuring a seamless and high-quality media experience.
Benefits of Optical Access
One of the main advantages of optical access is its ability to offer unified and intelligent network management. With products like Huawei’s OptiXaccess, businesses can significantly cut down on cabling and reduce physical footprint. Unified Network Management Systems (NMS) further simplify operations, making fault detection swift and efficient. This technology not only facilitates current network demands but also adapts to future requirements with ease.
What is Traditional Fiber and How is it Different?
Components of Traditional Fiber Systems
Traditional fiber systems involve the use of single-mode and multi-mode fibers, employing lasers and light detectors for data transmission. Components such as multiplexers, switches, and amplifiers support these systems. These elements work together to transmit data through light pulses across long distances.
Challenges with Traditional Fiber
While traditional fiber technology offers high-speed data transmission, it presents certain challenges. Deployment costs are higher due to extensive cabling and intricate infrastructure requirements. Maintenance also becomes complex, demanding specialized skills and resources. Moreover, the scalability of traditional fiber is limited compared to modern optical access solutions, posing challenges in areas with rising demand for high bandwidth.
Key Differences Between Optical Access and Traditional Fiber
Network Speed and Bandwidth Capabilities
Optical access technology generally provides superior speed and bandwidth. Solutions like Huawei’s MA5800 support 10G PON/GE/10GE shared platforms, offering robust multi-service virtualization, optimal for high-definition video and VR experiences. Traditional fiber systems can also offer high bandwidth, but deployment and network upgrades take more effort and time.
Deployment Challenges and Maintenance Costs
Optical access has the upper hand here with easier deployment and lower maintenance costs. Utilizing passive components reduces the need for continuous power and cooling, which lowers operational costs. Traditional fiber, meanwhile, involves more active components like optical amplifiers that require regular upkeep.
Flexibility and Scalability of the Systems
Optical access proves to be more flexible and scalable. It supports various business expansions, thereby reducing constraints on network growth. The distributed architecture of platforms like Huawei’s MA5800 also means smoother transitions and adaptability to future technological advancements. Traditional fiber’s scalability is more static, necessitating significant infrastructure updates to meet growing demands.
Impact on Long-Term Network Performance
Long-term performance is another area where optical access technology excels. Unified Network Management Systems (NMS) allow for intelligent operations and maintenance, which leads to better long-term performance. Traditional fiber networks require more intensive and frequent monitoring, making them less efficient over time.
Advantages of Optical Access Over Traditional Fiber
Faster and More Reliable Data Transmission
One of the most significant advantages of optical access is its ability to offer faster and more reliable data transmission compared to traditional fiber. Optical access technologies like Passive Optical Networks (PON) reduce latency, ensuring smoother performance for high-data-demand applications such as 4K streaming, cloud computing, and virtual reality. This increased reliability and speed make optical access ideal for today’s bandwidth-intensive digital experiences.
Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run
Although the initial deployment cost of optical access may be comparable to traditional fiber, the long-term cost-effectiveness is undeniable. The reduced need for maintenance, fewer physical connections, and simplified infrastructure result in lower operational costs over time. Furthermore, optical access minimizes the amount of cabling required, reducing both material and labor expenses. The efficiency gained through optical access provides substantial savings in the long run, making it a sustainable choice for network providers.
Greater Scalability and Future-Proofing
Optical access offers exceptional scalability, allowing networks to grow seamlessly as demand for bandwidth increases. Future-proofing is another major advantage, as technologies like 50G PON can be easily integrated into existing optical networks, ensuring that they remain relevant and capable of handling future data traffic. Systems like Huawei’s MA5800 support smooth upgrades to next-generation services, ensuring that networks can adapt to evolving needs without costly overhauls.
Conclusion
In summary, while both optical access and traditional fiber optic technologies have their merits, optical access stands out for its superior speed, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Solutions like Huawei’s OptiXaccess provide modern networks with the ability to meet today’s demands while adapting to future growth. For enterprises and service providers aiming at long-term efficiencies and lower costs, optical access is the way forward.